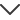
Vishay Dale RH01060R00FE02
Resistor;Wirewound;Res 60 Ohms;Pwr-Rtg 10 W;Tol 1%;Lug;Alum Housed;Military
Mfr. Part #: RH01060R00FE02 / RS Stock #: 70201456

Image may be a representation. See specs for product details.
Price
Qty.
Standard Price
1
$4.169
Additional Inventory
Product Specifications
Product Attribute
Attribute Value
Search
Element Material
Wirewound
Family Name
RH, NH Family
Package Type
Aluminum Housed
Packaging
Card Pack
Power Rating
10 W
Resistance
60 Ohms
Resistance Range
0 to 999 Ohms
Special Features
Military
Termination
Solder Lugs
Tolerance
1 %
Overview
The Vishay Dale MIL-PRF-18546 Qualified Wirewound Resistors have a complete welded and molded construction for total environmental protection. These resistors mount directly onto a chassis to utilize heat-sink effect. This range of wirewound resistors offers high stability at conventional power ratings and flat marking surface for easy identification.
Features:
-? Molded construction for total environmental protection
-? Resistance Tolerance 1%
-? High-temperature silicone coating or encapsulate
-? Complete welded construction
-? Meets applicable requirements of MIL-PRF-18546
-? Available in non-inductive styles (type NH) with Ayrton-Perry winding for lowest reactive components
-? Mounts on chassis to utilize heat-sink effect
-? Excellent stability in operation (< 1 % change in resistance)
Applications:
-?DC/DC converters
-?AC/DC inverters
-?High-voltage bleeders
-?Dynamic braking
-?Bias supply
-?Motor speed controls
-?Voltage divider networks
-?Filament dropping
-?Capacitor charging/discharging regulation
-?Voltage dropping
-?Electrical loads
-?Crow-bar circuits
-?Current shunts






 Bulk pricing available
Bulk pricing available
